BRM-203: The Breakthrough Invention
The Aim:
Continuous dopaminergic stimulation (CDS) helps to alleviate motor dysfunctions (on/off, LD induced dyskinesias) in PD patients.
The Situation
Oral sustained release formulations failed to generate steady-state LD plasma levels.
Duo-DOPA® is an intra-intestinal gel infusion needing a prior surgical intervention. The CDS aim is reached with large variances.
New Developments using subcutaneous Infusions
Neuroderm´s (ND-0612H) subcutaneous infusion makes use of pH-dependent solubility of LD. Treatment needs 2 infusion sites. Due to rather restricted daily doses, oral add-on treatments seem to be necessary. ND-0612H clearly fails the CDS aim. Significant local side effects are reported. The mass ratio of LD to CD is 8:1.
AbbVie´s Pro-Duodopa® is able to generate steady-state LD plasma levels. Comparably low inhibition of AADC is achieved by sc-coadministration of FCD. The mass ratio of FLD to FCD is 20:1. Whereas FLD is not patentable, the combination of FCD/FLD is.
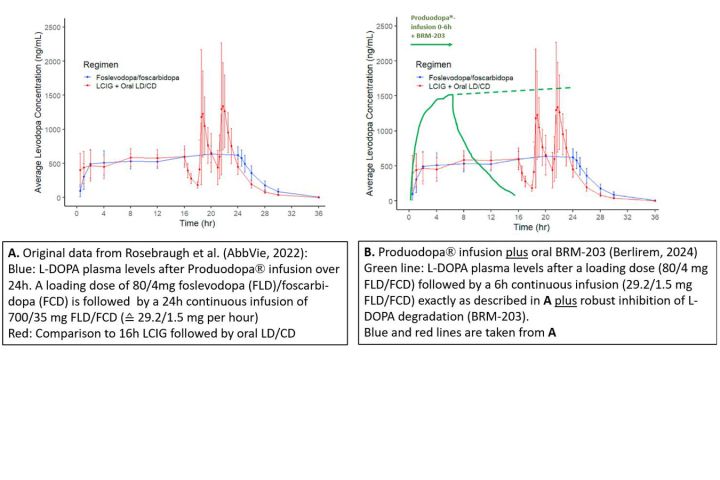
BRM-203 achieves a breakthrough by reducing the LD dose, that needs to be given by sc-infusion. As shown by Phase I studies LD plasma levels were increased up to threefold by oral inhibition of main biotransformation pathways (AADC and COMT). By this (patented) invention, the daily LD-dose given by sc-infusion was reduced to a level that is locally well tolerated with only one infusion site.
To visualize the invention the following Figure (composed of our data and published ones) can serve: